Impact Test
The notched bar impact test (ASTM E23, BS EN 10045, ISO 148-1 and IS 1757, IS 1598) is a method for evaluating the toughness and notch sensitivity of engineering materials. It is typically used to determine the energy required for the material to deform before fracture, i.e., the toughness of metals, but similar tests are also used for polymers, ceramics, and composites. Metals industries include oil and gas, aerospace, power generation, automotive, and nuclear.
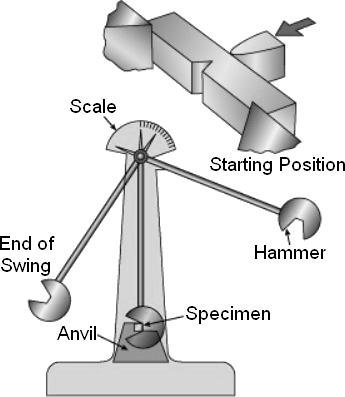
The notched specimen is broken by the impact of a heavy pendulum or hammer falling at a specified speed over a specified distance. During testing, the energy absorbed by the fractured specimen is measured.
The Tests We Offer:
IZOD Test:
We take a specimen with one or more notches, machine it to a square or round section, and secure it vertically. Then, we give it a good whack with a hammer to see how much energy it absorbs before breaking.
Charpy Test:
Similar to the IZOD test, but with a “V” or “U” notch, the specimen is machined to a 10mm x 10mm cross-section. If your material is thinner, we use a smaller specimen. We can even run the test at cryogenic temperatures to see how the material behaves in extreme cold.
How It Works:
We place the notched specimen in the path of a heavy pendulum or hammer, which swings down at a specific speed and distance. When the specimen breaks, we measure the energy it absorbed. This tells us how tough your material is and how it will likely perform in real-world scenarios.
Why This Matters:
Knowing your material’s toughness can make all the difference in critical applications. Whether you’re building an airplane, a car, or an oil rig, you need to know your materials won’t fail when it counts.
Why Trust Om Metalab?
With years of experience and top-notch equipment, Om Metalab delivers precise and reliable results. We follow industry standards like ASTM E23, BS EN 10045, ISO 148-1, IS 1757, and IS 1598, so you can be confident that your materials are up to scratch.
Standards we tested to
Sr No | Discipline: Impact Test | Test Methods |
1 | Charpy U Notch | ASTM E23: 2018, IS 1499: 2003, IS 1757-1: 2020, ISO 148-1: 2016 |
2 | Charpy V Notch Impact Test | ASTM E23: 2018, ASTM A370: 2022, ISO 148-1: 2016 |
3 | Izod Impact Test | IS 1598: 2020 |

IZOD
The test specimen has one, two, or three notches and is machined to have a square or round section. The specimen is positioned on the anvil with the notch facing the hammer and is secured vertically.
Charpy
A test specimen with either a “V” or “U” notch is machined to a 10mm x 10mm (full size) cross-section. Where there are limitations on material thickness, sub-size specimens are used. Cryogenic temperatures can be used to evaluate samples.
